This is an internal documentation. There is a good chance you’re looking for something else. See Disclaimer.
Setup a DevOps Work Machine
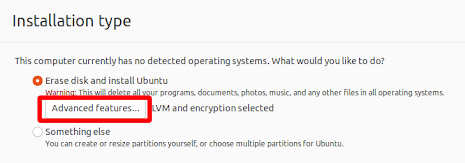
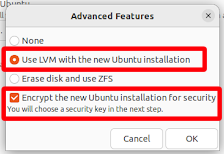
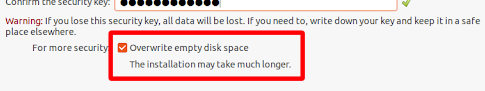
Enable Full Disk Encryption (FDE)
Important
Simply enabling encryption for your home directory is not enough.
If you already installed your OS and it doesn’t allow enabling FDE after installation, reinstall. No exceptions!
Remember that you need to type the selected passphrase on every boot. Select a reasonably-easy-to-type passphrase.
Example, enabling FDE on Ubuntu 22.04:
Set up SSH
Create a Key
ssh-keygen -t ed25519
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub # copy key and paste in the next step
Distribute Key
You also want to give the content of ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub to someone of operations. To that regard, you can post the public key in the Operations Public channel and ask for it to be granted access.
Tip
For admins: How to allow access is documented in Server Access (SSH/KVM/noVNC)
Setup Tocco Repository (Debian-Based Systems)
Public key: Tocco repo public key
Debian / Ubuntu
Hint
Currently supported distributions:
Debian bookworm / trixie
Ubuntu noble
Add repository and install tocco-metapackage:
curl https://docs.tocco.ch/_static/download/tocco-repo-keyring.asc | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/tocco-repo-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
sudo tee <<<"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/tocco-repo-keyring.gpg] https://mirror.tocco.ch/repos/apt/tocco $(lsb_release -cs) main" /etc/apt/sources.list.d/tocco-repo.list >/dev/null
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y tocco-metapackage
Set up Wireguard VPN
Note
macOS users use instructions in Set up Wireguard VPN (Mac Edition) instead.
Configure VPN
Install Wireguard:
apt install wireguard wireguard-tools
Generate private / public key pair:
(private=$(wg genkey); public=$(wg pubkey <<<$private); echo "private_key: $private; public_key: $public")
Submit the public_key to Operations Public channel and ask to be granted VPN access.
Make sure you keep the private_key, you’ll need it.
You’ll get a VPN config back. Replace the XXX placeholder in it with your private_key and then store it at /etc/wireguard/wg-tocco.conf.
Important
This is a per-device key. Generate a fresh key if you need access on an addational device. Using the same key on two devices will not work.
Tip
For admins: see Wireguard VPN.
Test VPN
Enable VPN:
wg-quick up wg-tocco
Test connection:
ping -A -c 3 10.148.60.1 ping -A -c 3 2001:8e3:5396:c9b::1 ping -A -c 3 tocco.ch
Disable VPN:
wg-quick down wg-tocco
Setup Git
Install Git
Debian-Based Systems
Already installed.
OSX Systems
If you are running OSX, you have git already installed. You can check the installed version using git -v.
If the installed version is not to your liking (or you are unable to update your OSX for some reason), you can create a separate git installation using brew and keep that on the version that you prefer. Brew will overwrite the linking of the git command for you, so that the brew version will be executed instead of the system version.
Configure Git
git config --global user.email "${USERNAME}@tocco.ch" # replace ${USERNAME} with pgerber, …
git config --global user.name "${YOUR_NAME}" # replace ${YOUR_NAME} with "Peter Gerber", …
Ignore some files in all repository by default:
Debian-Based Systems
mkdir -p ~/.config/git
cat >>~/.config/git/ignore <<EOF
.idea/
*~
.*.swp
EOF
OSX Systems
The first command creates a new global gitignore file and the second command tells your git to use this new file for global ignores.
touch ~/.gitignore_global
git config --global core.excludesfile ~/.gitignore_global
cat <<EOT >> ~/.gitignore_global
.DS_Store
.idea/
EOT
Configure SSH
Configure user name:
cat >>~/.ssh/config <<EOF # First entry wins. So, override settings here, at the top. Host *.tocco.cust.vshn.net User \${FIRST_NAME}.\${LAST_NAME} # Comment in if you want to login as 'tadm' by default instead as 'tocco' (root permissions required). # Host *.tocco.ch # User tadm EOFReplace ${FIRST_NAME}.${LAST_NAME} like this: peter.gerber.
Note
Non-Debian-based systems only (DragonFly BSD, Fedora Linux, FreeBSD, Hurd, Illumos, etc.):
Clone the tocco-dotfiles repository:
cd ~/src git clone https://gitlab.com/toccoag/tocco-dotfiles.gitLink
authorized_keys_toccointo SSH config directory:mkdir -p ~/.ssh ln -s ~/src/tocco-dotfiles/ssh/known_hosts_tocco ~/.ssh/Adjust the path if your repository clone is located elsewhere.
Include config and set user name:
cat >>~/.ssh/config <<EOF Host * Include ~/src/tocco-dotfiles/ssh/known_hosts_tocco EOF
Setup IDEA
Install IDEA
Download the latest version and extract it:
cd ~/Download
wget https://download-cf.jetbrains.com/idea/ideaIC-XXXX.X.X.tar.gz
cd ~/install # or wherever you want to install it
tar xf ~/Download/ideaIC-XXXX.X.X.tar.gz
ln -s ~/Download/ideaIC-XXXX.X.X idea
mkdir -p ~/bin
ln -s ~/install/idea/bin/idea.sh ~/bin/idea
rm ideaIC-XXXX.X.X.tar.gz
If an update is released that forces you to download a new *.tar.gz file, extract it and replace the link
in ~/install/ using ln -sfn ideaIC-XXXX.X.X idea.
Hint
This assumes that ~/bin is in your $PATH which is the case on most Linux-based systems. If you had
to create ~/bin, you may have to close and reopen the terminal for it to be added to $PATH.
If necessary, add it manually to $PATH by adding this to ~/.profile:
export PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
Create Desktop Entry
open idea and find Tools → Create Desktop Entry… (or Configure → Create Desktop Entry… on
the welcome screen).
Change default encoding for properties files
Open File → Settings → Editor → File Encodings and change Default encoding for properties files to UTF-8
Disable creating run configuration automatically
Open File → Settings → Languages & Frameworks → Spring and disable Create run configuration automatically
Increase Memory Available to IDEA
Help → Edit Custom VM Options…
Say Yes to create a config file
Set max. memory (-Xmx) to something sensible (e.g. -Xmx3096m)
Increase Watch Limit (Linux only)
Create the file /etc/sysctl.d/50-idea.conf with the following content:
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=524288
Then load it with this command:
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/50-idea.conf
Install Java
Required Java versions:
Java Version
Nice Versions
17
3.1 - 3.9
21
3.10 - 3.14
25
3.15
Debian-Based Systems
Use Eclipse Temurin builds provided Adoptium
Alternative sources:
Debian-only:
Most recent Java LTS version are usually available via backports:
cat >>/etc/apt/source.list.d/backports <<EOF deb https://deb.debian.org/debian $(lsb_release -cs)-backports main EOF apt update # install Java 11 apt install openjdk-11-jdk
Setup Gradle
There is no installation of gradle necessary as the gradle wrapper is used.
Repository Access
Create a file ~/.gradle/gradle.properties and copy the content from Bitwarden.
Increase Max. Number of Open Files
Create /etc/security/limits.d/open_file_limit.conf with this content:
* - nofile 1000000
Hint
Only effective once you logged out and in again.
Install Dependencies
On Ubuntu install the following dependencies:
apt install libjpeg62 libpng16-16
(there libraries are dynamically loaded by wkhtmltopdf)
On Ubuntu 22.04 and newer install the following dependencies. If there is a newer version released already, the version numbers in the command need to be adjusted.
wget http://nz2.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/o/openssl/libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2.23_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2.23_amd64.deb
This fixes the issue “cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory”.
On macOS add the gradle property wkhtmltopdfClassifier=osx to ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
GitLab Account
-
You can create/reuse your personal account or create a Tocco-specific one. This is up to you.
-
Retrieve key:
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub -
You can use an authenticator app like 2FAS / Aegis for this or a U2F device (if you own one).
Publish your username in the Slack channel public_operations and ask to be added to the group toccoag.
Clone and Build Nice2
Download repository
git clone git@gitlab.com:toccoag/nice2.git
Build nice
Test if Gradle build works:
cd ~/src/nice2
./gradlew build -x test
Create IDEA Project (Nice2 Integration)
open idea and find File → New → Project from Existing Sources… and follow the steps described below
select root directory of your nice2 clone (e.g.
~/tocco/src/nice2-2.25)click OK
choose option Import project from external model → Gradle
click Finish
open new project either in a new window or in the existing window
Tip
It is recommended to create different git clone and idea project for each available version. For example one clone and project for master, one for v2.24, one for v2.25 and so on.
Hint
Note that there is already a run configuration for customer test ready to use (called “Start Nice2 (customer ‘test’)”).
If you need to run a different customer, just duplicate that run config and change the directory in the field Gradle project to your customer.
The Nice instance gets a max memory of 1.2G (see -PjvmArgs=’-Xmx1200m’ in the run command in the run config). If this isn’t enough for your task at hand, you can increase the max memory by changing the number in the run config.
Caution
However, you shouldn’t carelessly increase the number if you’re running out of memory locally - it is probable that there’s something wrong, as 1.2G should be plenty enough to run any process within the Nice instance.
Setup OpenShift Client
Install Client
On Debian / Ubuntu this is already installed.
Tip
MacOs:
If you are running MacOS, just run brew install openshift-cli and ignore the rest of this chapter.
Install Docker (Optional)
Debian-based (e.g. Ubuntu):
apt install -y docker.io
Everyone else, find your OS here, follow the instructions, and hope for the best.
S3 Access Key
Ask operations (e.g. via Operations Public channel) to issue you an access key for our S3 storage.
Once you retrieved the key, add it to ~/.aws/credentials like this:
[nice2]
aws_access_key_id=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
The section must be called nice2, the name is hardcoded in Nice2.
Tip
For admins: how to issue a key is described in Create User.
S3 Access via s3cmd (Optional)
Install s3cmd:
apt install s3cmd
Configure s3cmd:
s3cmd --configure
Select the default for all options.
Adjust the following configuration entries in ~/.s3cfg:
[default]
access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
secret_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
host_base = objects.rma.cloudscale.ch
host_bucket = %(bucket)s.objects.rma.cloudscale.ch
The access and secret keys are the keys you obtained in the previous step.
Test access:
s3cmd info s3://tocco-nice-test >/dev/null
# no output expected
Setup Ansible
Hint
The following instruction have been tested on Debian / Ubuntu, for other operating systems make sure you have this installed:
Python3
Ansible >= 7.7
Various Python packages. See python3-* dependencies in tocco-metapackage’s CONTROL file for a up-to-date list.
Clone the repository:
mkdir -p ~/src cd ~/src # Access to group "toccoag" required git clone git@gitlab.com:toccoag/ansible.git
Get Ansible Vault password(s)
Ansible Vault is used to store sensitive data (password, API keys) encrypted. You need a password to access them.
There is two Vaults:
One Vault that expects a file containing the password at
~/.ansible-password. This Vault is needed for server management and you generally only need it if you’re a part of the operations team.The second Vault expects a file containing the password at
~/.ansible-tocco-password. This Vault is need to manage our application and is generally needed by devs and ops.
Ask one of your colleagues to get the Vault passwords and store in said files. Be sure to set proper permission on the files:
(umask 0077; echo ${PASSWORD_GOES_HERE} >~/.ansible-password) (umask 0077; echo ${PASSWORD_GOES_HERE} >~/.ansible-tocco-password)
Setup Postgres
Install Postgres:
sudo apt install postgresql
Note
If you are running macOS, it is recommended that you install the multi-version app. This app allows you to run multiple postgres versions simultaneously and makes switching between versions easy. To install this app, browse to https://postgresapp.com/downloads.html and download the first installer under “Additional Releases” called “Postgres.app with all currently supported versions (Universal/Intel)”.
Setup Postgres for use with Ansible:
sudo apt install zstd sudo -u postgres psql -c "CREATE ROLE \"$(id -un)\" WITH LOGIN SUPERUSER" psql -c "CREATE DATABASE \"$(id -un)\"" postgres
The above is required to make sure Ansible can be used to copy databases. This creates a Postgres user with admin rights and with the same name as the Linux user. This allows to login via Unix socket without providing credentials.
Setup Postgres for local development
Initially create role and user:
CREATE ROLE nice_local WITH LOGIN SUPERUSER PASSWORD 'SET_YOUR_PASSWORD';
Add an
application-development.propertiesfile to the customer (pathcustomer/NAME/src/main/resources):hibernate.main.serverName=localhost hibernate.main.user=nice_local hibernate.main.password=SET_YOUR_PASSWORD
See Copy Database on how to copy a database to your local postgres server. If the database name is not the same as defined in
application.propertiesalso sethibernate.main.databaseName.Create a global nice2 application property file (optional)
You can create a global nice2 application property file at
~/nice2-application.propertiesto define properties that are valid for all customers and all versions. For example the local database user and password or the gotenberg credentials can be defined here.Note
If a property is defined in multiple files, the first occurrence wins:
~/nice2-application.propertiesapplication-development.propertiesin the customer folderapplication.propertiesin the customer folder
In the committed run config (start nice2 and db refactoring) the path to the global application property file is configured. Just duplicate this run config and adjust the gradle project to the customer you want to run!
Setup tco (Optional)
Installed already on Debian / Ubuntu.
tco is a helper tool for anyone and contains many useful commands.
Setup Tocco Client (Optional)
See Setup
Setup Thunderbird as Mail Client (Optional)
Personal Inbox
Enter your full name
Enter mail address (<your-name>@tocco.ch)
Skip password
Select Configure manually
Use these settings:
Incoming server:
protocol: IMAP
server name: outlook.office365.com
port: 993
security: SSL/TLS
authentication method: OAuth2
Username: <your-name>@tocco.ch
Outgoing server:
protocol: SMTP
server name: smtp.office365.com
port: 587
security: STARTTLS
authentication method: OAuth2
Username: <your-name>@tocco.ch
Click Done
Enter your password
Check all Folders for Incoming Mail
If you wish for Thunderbird to check all folders for mail:
Go to Preferences → Advanced → General → Config Editor…:
Set mail.server.default.check_all_folders_for_new to true.
admin@tocco.ch Inbox (DevOps / Admins Only)
admin@tocco.ch is a shared inbox used by Operations.
Open Account Settings
Account Actions → Add Mail Account…
Enter your full name
Enter admin@tocco.ch as mail address
Skip password
Select Configure manually
Use these settings:
Incoming server:
protocol: IMAP
server name: outlook.office365.com
port: 993
security: SSL/TLS
authentication method: OAuth2
Username: admin@tocco.ch
Outgoing server:
protocol: SMTP
server name: smtp.office365.com
port: 587
security: STARTTLS
authentication method: OAuth2
Username: admin@tocco.ch
Click Done
Select Sign in with other account and use your regular username (i.e. <your-name>@tocco.ch) and password to log in.