This is an internal documentation. There is a good chance you’re looking for something else. See Disclaimer.
Add Non-Customer Module
Adding a new module contains the following steps:
Nr |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
✔ |
|
2 |
✔ |
|
3 |
||
4 |
||
5 |
✔ if 3 is done |
Add Module in Backoffice
Each existing module (core, optional and core) must be documented in our Backoffice. This is important because depending on the documented modules the dependencies will be generated for customer modules.
Open the Entity
Modulein the backoffice
Create a new Module entitiy
Set a good technical name. The technical name should be the same as it will be called in the folder structure of the nice project
Set the correct type of the module. One of
core,optional,customerorbetween.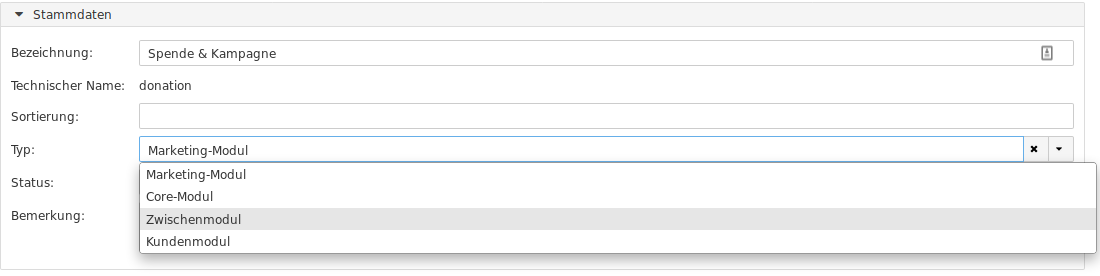
Add all required modules. Depending modules are all modules which are used by the new module. This is important because if this module later is added to a customer all depending modules also need to be added to the customer.
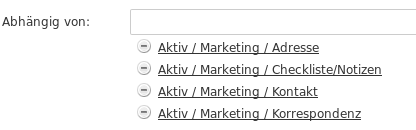
Create Basic Folder Structure
A new customer module can be created using the command gradlew createNewModule -P moduleType={core, optional} -P moduleName=<name>.
This command creates the necessary folder structure and project files and registers the new module in the settings.gradle file.
Core modules are also automatically added to the generic :customer module so that they are included for every customer.
Optional modules are automatically added to the test (and some other) customer.
Add Content to module Folder
Inside the module folder optional/${MODULE}/resources different folders which configure the module can
be added. Here are the most common use cases:
model
The model folder must be added as soon as you need to
add or adjust entities or relations -> see Entities and Relations
add or adjust text resources -> see Text-Resources
add or adjust forms (list, search, detail) -> see Forms
add or extend a menu (settings or modules) -> see Menu
add reports -> see Reports
db Inside the db folder changesets are placed. See document Changesets.
acl Inside the acl folder all acl rule files are located. See chapter ACL
resources Inside the resources folder JS files are placed. For actions and public flows.
outputtemplate Inside this folder FTL templates are placed which for example can be used for reports.
Add Java Source Folders
Java code (e.g. listeners, actions, services, rest-resources, …) can just be added to the src/main/java folder of
the module. We usually separate the code into the 3 packages impl, api and spi.
api -> defines services which can be injected by other modules
spi -> defines classes which other modules can use or extend.
impl -> the implementation of the module specific Java code
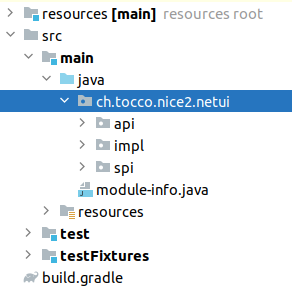
To be able to access classes of api or spi in other modules, all packages must be listed as exports in
module-info.java
open module nice.core.netui {
exports ch.tocco.nice2.netui.api.actions;
exports ch.tocco.nice2.netui.api.actions.security;
// ... mode exports / imports
}
Include Resources in Archive
build.gradle defines which resources will be included in the generated archive. By default all files / file patterns
defined in ext.resourceIncludePattern of the root build.gradle are included. If module requires additional files
this must be declared on the “top level” of the module specific build.gradle.
resourceIncludePattern << 'resources/font/*'
resourceIncludePattern << 'resources/reporting/*.ftl'
dependencies {
//...
}
Country-specific Module
If only changes to text resources are required, these can be directly done in the base module with the file language_de_DE.properties (See Different orthography for germany).
For changes that go beyond this, an additional, Germany-specific module is created, which extends the base module.
The Gradle module name should match the pattern optional|core:[country]:[module]-[country].
The Germany-specific module for the optional:address module is therefore named optional:de:address-de.
The module name in module-info.java should match the pattern nice.optional|core.[module].[country].
The module-info.java for the Germany-specific module address looks like:
open module nice.optional.address.de {
requires nice.optional.address;
}
Text resources work as usual in country-specific modules.
The only difference is that the German file should be named language_de_DE.properties (There will be no language_de.properties).
If you just want to change German texts you can use # nice2validate stop validation -- textresources below this point will not be validated.
as else all language files must contain all text resources keys.
Back Office
For modules of the type customer module, the country in which the respective customer is based is set. If no country is set, Switzerland is used as default.
For modules of the types core, marketing and intermediate several countries can be selected. If there is a Germany-specific module for the address module, Germany is selected in the country field of the country-specific module in the back office. In the base module address the address-de module is added as “country-specific module variants”.