This is an internal documentation. There is a good chance you’re looking for something else. See Disclaimer.
Form Field
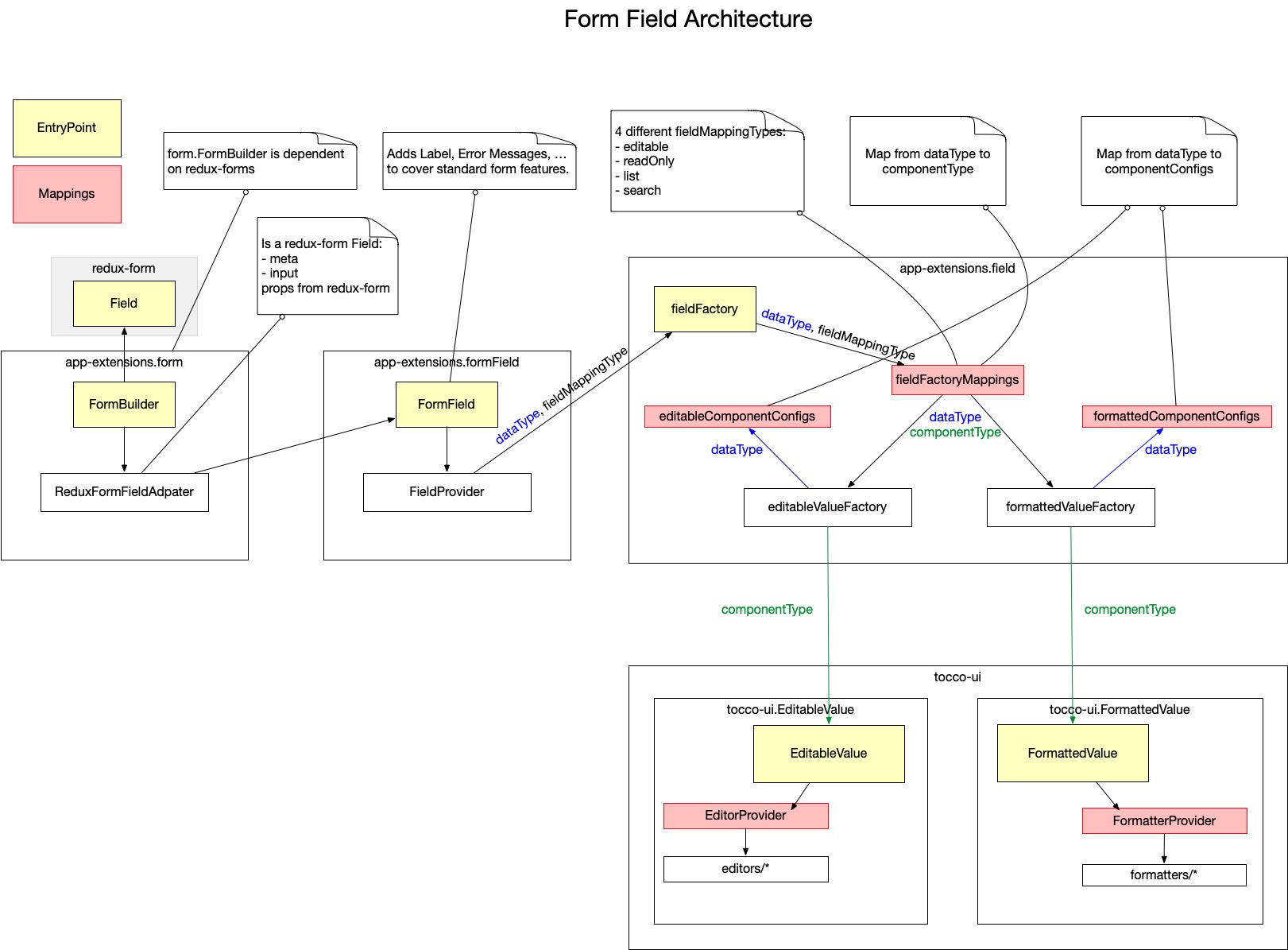
The form field architecture used in the admin package contains a lot of different wrappers and maps. The section should give a rough overview about the architecture.
Glossary
dataType- Tocco form field dataType (e.g.'counter')componentType- Client component type that maps to a component (e.g.'select')fieldMappingType- Defines different dataType to componenType mapping per each fieldMappingType ('readOnly'|'editable'|'list'|'search')componentConfig- Config that gets passed to the componentcomponent- React component for specific input / value element (e.g.DateEditorDateFormatter)
Packages
tocco-uicontains all form field UI components
redux-form independent
dataType unaware only knows componentType
app-extensions.fieldcontains a mapping per form type (readOnly, editable, list, search)
mapping maps dataType to componentType (e.g. ‘counter’ maps to ‘integer’ for ‘editable’ fieldMappingType)
app-extensions.formFieldadds label, error messages and all styling on top of app-extensions.field for having a complete form field
app-extensions.formcreates redux-form.Field from app-extensions.formField
Mappings
There are two different mappings dependent on dataType:
dataTypetocomponentTypeis defined in
fieldFactoryMapping.jsto define which UI component should be used
dataTypetocomponentConfigis defined in
(formatted|editable)ComponentConfigs/index.jsto be able to provide a specific config for the UI component
Therefore it could be that the same component is used with different component configs or vice verca that the same component config is used for different components.
Examples:
Same component config but different components:
multi-select-boxandsingle-select-boxdataTypes useselectcomponent config butmulti-select-boxmaps tomulti-selectcomponent andsingle-select-boxmaps tosingle-selectcomponent.Same component but different component configs:
counterandlongdataTypes map tointegercomponent butcounterusesnumbercomponent config andlongusesintegercomponent config.
Event handling
redux-form passes event handlers to the field component (ReduxFormFieldAdapter).
The event handlers are passed down to EditorProvider which attaches it to the component container div.
In order to overwrite the default behaviour the specific event has to be attached to the DOM in the edit component.
By calling event.stopPropagation() the event bubbling can be stopped and the default event handler will not get called.
Example:
const suffixer = val => `${val}-suffix`
const MySuffixEdit = ({value, onChange, events}) => {
const handleBlur = event => {
if (typeof events?.onBlur === 'function') {
events.onBlur(suffixer(event.target.value)) // do not save value as is, always apply suffix
}
event.stopPropagation()
}
return (
<input type="text" value={value} onChange={onChange} onBlur={handleBlur} />
)
}
onBlur event handler
The default onBlur handler by redux-forms sets the text value of the event target as the new value when blurring the input field.
This causes problems as soon there are some non-text value components. Therefore the onBlur handler is overwritten in the EditorProvider for all form field to always use the current field value.
Pseudo form fields
Sometimes it is necessary to have a fake form or additional fields in a form which does not really exist in the entity model.
Such fields are called pseudo fields as the backend does not know them. A part from regular data types such as text or string
you can add single and multi selection fields with the data type choice. The form package provides helper methods to create fields
with createXXXXXXXField (e.g. createMultipleChoiceField see (See JSDoc for all helper methods) and to create answer options for choice fields with createChoiceOption.
Such fields are normally synchronous validated. For the choice data type is a special syncTypeValidator implemented.
The asynchronous validation removes these pseudo fields before sending the request to the backend.
Each pseudo field object (returned by createXXXXXXXField) have two parts formField the form field definition and entityPath which should be added to the entity path of the regular entity.
The following steps are required to use pseudo fields with the form builder:
Create a list of pseudo fields (here named
pseudoFields) with the helper methodscreateXXXXXXXField(e.g.createMultipleChoiceField)Combine all form field definitions
pseudoFields.map(f => f.formField)and add them the the regular form definition (e.g. usereplaceBoxChildren)Combine all entity paths to a single object with
getMergedEntityPaths(pseudoFields)(here saved in variablemergedEntityPaths)(Update case only) if you use
rest.fetchEntityin combination withform.getUsedPathsyou must exclude the pseudo fields (e.g.yield call(form.getUsedPaths, fieldDefinitions, field => field.pseudoField !== true)) else the backend throws an error due to unkown paths(Update case only) after fetching the entity (saved in variable
entity) combine them with the pseudo field entity pathsentity.paths = {...entity.paths, ...mergedEntityPaths}(Create case only) the entity paths must be transformed to form values as no entity paths are loaded. This can be done with:
const defaultValues = yield call(form.getDefaultValues, fieldDefinitions)
const entityValues = yield call(api.getFlattenEntity, {model: 'MODEL', paths: {...mergedEntityPaths}})
const formValues = yield call(form.entityToFormValues, {...entityValues, ...defaultValues}, fieldDefinitions)
Now you can initialize redux with
yield put(formActions.initialize(REDUX_FORM_NAME, formValues))(Note: if you call the redux initialize event before adding the pseudo fields the initial values are not set correctly)If the form is submitted you can split the form values in to the regular entity and pseudoFields with
splitFlattenEntitywhich returnsentityandpseudoFields. For example:
const flatEntity = yield call(form.formValuesToFlattenEntity, formValues, fieldDefinitions)
const splittedFlatEntity = form.splitFlattenEntity(flatEntity, fieldDefinitions)
const regularEntity = yield call(api.toEntity, splittedFlatEntity.entity)
// do something with splittedFlatEntity.pseudoFields